| English Wikipedia - The Free Encycl... |
Euclidean vector
In mathematics, physics, and engineering, a Euclidean vector (sometimes called a geometric or spatial vector, or—as here—simply a vector) is a geometric object that has magnitude (or length) and direction and can be added to other vectors according to vector algebra. A Euclidean vector is frequently represented by a line segment with a definite direction, or graphically as an arrow, connecting an initial point A with a terminal point B, and denoted by 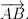
| See more at Wikipedia.org... |
© This article uses material from Wikipedia® and is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License and under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License
